머리
랜덤하게 나오는 듯 하지만, 잘 겹치지는 않는 그런 방식이 필요했던적이 있었습니다.
근데 찾아보니 저-불일치-순열 이라는 몇몇 정보가 나와서 그냥 작성했습니다.
아참 맨마지막 sobol로 만든 3차원 난수적용 공간을 퍼스펙으로도 찍어봤습니다.
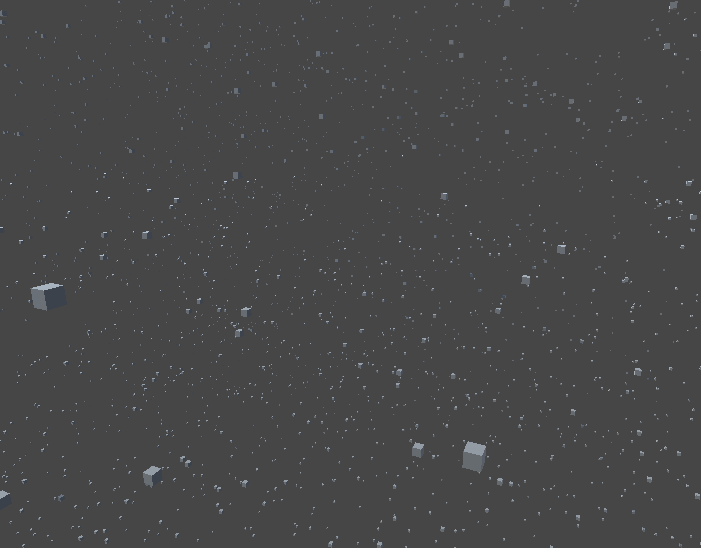 우주같고 이쁘지않나요?(먼지같다는 뜻)
우주같고 이쁘지않나요?(먼지같다는 뜻)
몸
일단 저불일치 순열도 몇개가 있는데
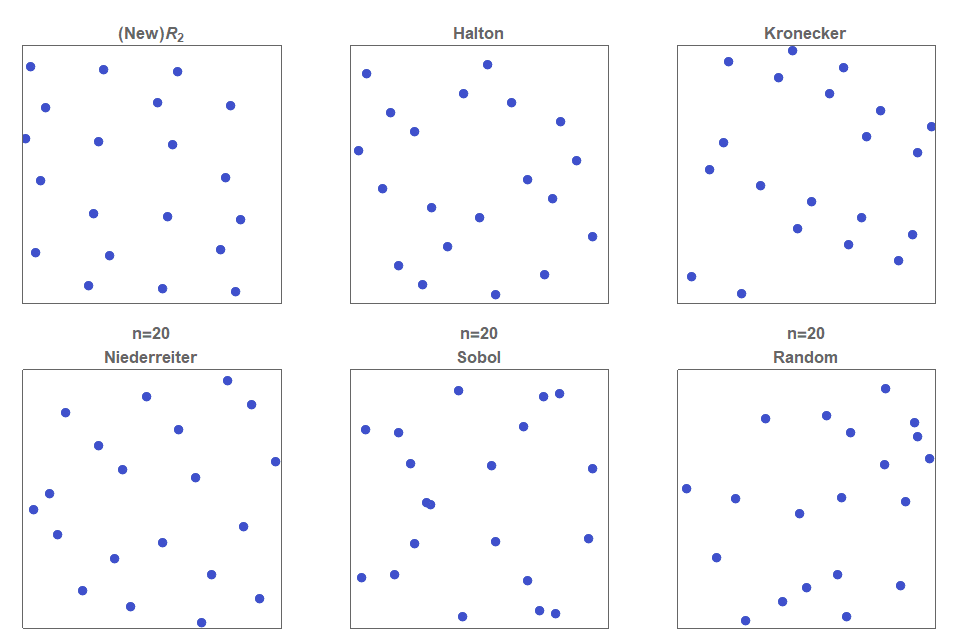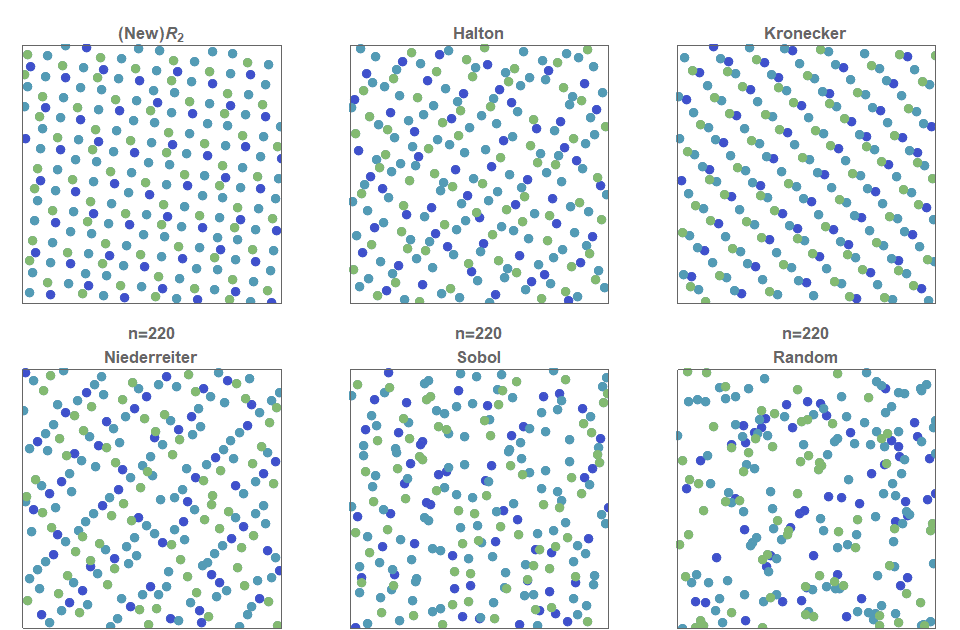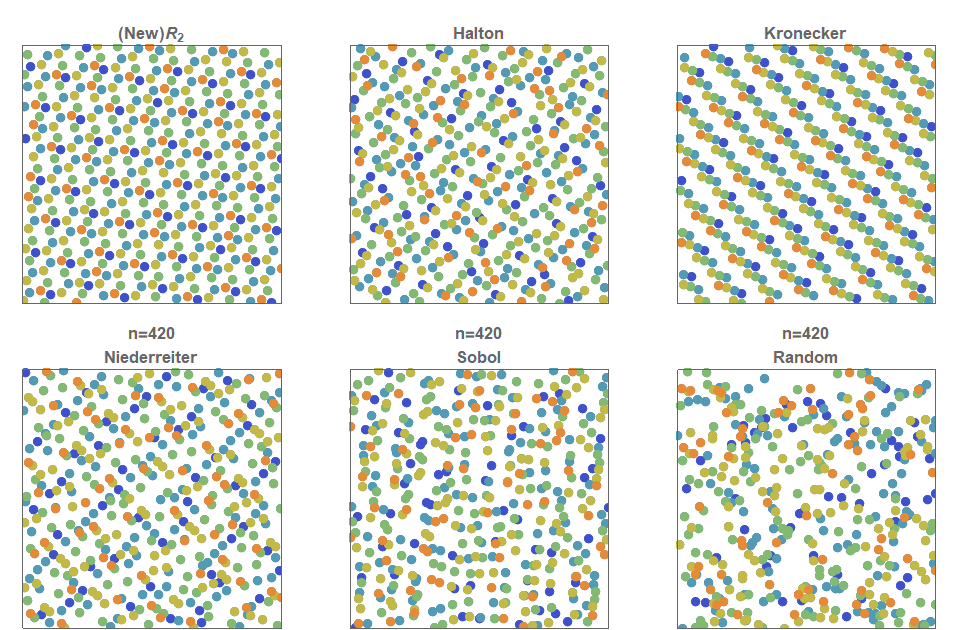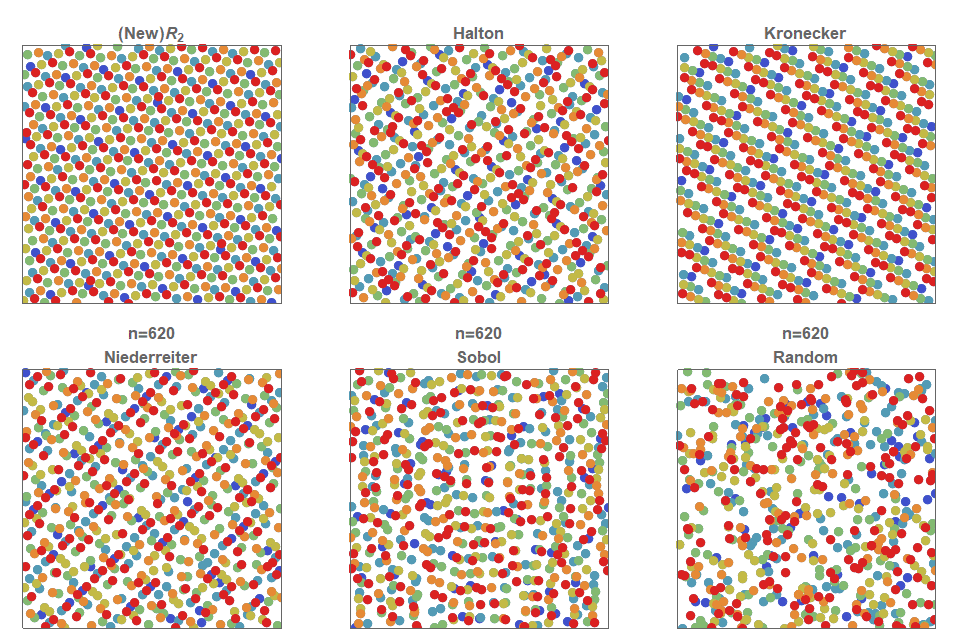
그래도 좀 난수같아보이는 halton과 sobol을 대상으로 정했습니다.
Halton sequence
무우우려 유니티에 포함되어있는 코드긴 합니다.
그리고 단순하게 구현할 수 있습니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
public static float Get(int index, int radix)
{
float result = 0f;
float fraction = 1f / radix;
while (index > 0)
{
result += (index % radix) * fraction;
index /= radix;
fraction /= radix;
}
return result;
}
테스트코드는 다음과 같이 구성했습니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEditor;
using UnityEngine;
public class CustomButton : DevMono
{
private List<GameObject> instances = new List<GameObject>();
private IEnumerator currentRoutine;
[Button]
void AddEditLoop()
{
EditorApplication.update += EditorUpdate;
}
private void EditorUpdate()
{
currentRoutine?.MoveNext();
}
[Button]
private void GenerateCubesViaHalton()
{
currentRoutine = GenerateCubes();
IEnumerator GenerateCubes()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 100; ++i)
{
var instance = GameObject.CreatePrimitive(PrimitiveType.Cube);
var pos = new Vector3(Get(i, 2), Get(i, 3), Get(i, 5));
instance.transform.position = pos;
instance.transform.localScale = Vector3.one * 0.1f;
instances.Add(instance);
yield return null;
}
}
}
[Button]
private void ReleaseEditLoop()
{
EditorApplication.update -= EditorUpdate;
}
[Button]
private void Delete()
{
foreach(var instance in instances)
{
DestroyImmediate(instance);
}
instances.Clear();
}
//Halton
public static float Get(int index, int radix)
{
float result = 0f;
float fraction = 1f / radix;
while (index > 0)
{
result += (index % radix) * fraction;
index /= radix;
fraction /= radix;
}
return result;
}
}
Radix는 기저인데, 소수를 사용합니다.
저차원 저갯수에서는 작은 소수를 사용해도 무방합니다.

Sobol Sequence
고차원을 위한 - 귀찮고, 많고, 복잡합니다.
솔직히 처음 만든게 halton이였다면, 소볼은 안건들였을 것 입니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
internal class SobolSequence : IEnumerable<float>
{
public class SobolEnumerator<T> : IEnumerator<float>
{
protected List<SobolSequence> seq;
private SobolEnumerator() { }
public SobolEnumerator(in SobolSequence seqeuence)
{
seq = new List<SobolSequence>();
seq.Add(seqeuence);
for (int i = 1; i < seqeuence.s; ++i)
{
seq.Add(new SobolSequence(seqeuence.s, seqeuence.a, seqeuence.m));
}
}
public IEnumerable<float> Current => seq.Select(s => (float)s.Current);
object IEnumerator.Current => seq.First().Current;
float IEnumerator<float>.Current => (float)seq.First().Current;
public bool MoveNext()
{
foreach (var s in seq)
{
s.MoveNext();
}
return true;
}
public void Reset()
{
foreach (var s in seq) s.Reset();
}
public void Dispose()
{
seq = null;
}
}
/// <summary>
///
/// </summary>
/// <param name="s">Dimenstion</param>
/// <param name="a">coefficients</param>
/// <param name="m">Seeds</param>
/// <exception cref="InvalidOperationException"></exception>
public SobolSequence(int s, ulong a, IList<ulong> m)
{
this.m = m.ToArray();
// store the binary sequence that encodes our direction-generating recurrsion
// we could do this with a single ulong, but the literature typically specifies
// the degree s seperately from the coefficients of x^{s-1}, \cdots, x^2 x^1, which
// are stored as binary digits in a = (a_{s-1} \cdots a_2 a_1)
this.s = s;
this.a = a;
// now we construct the "directions"
// The ith direction number v_i = u_i / 2^i, where u_i is an whole number with fewer
// than i bits.
// we will store the v's scaled up by a constant factor 2^n, where n is the maximum i, so they
// can be manipulated as whole binary numbers; then we will divide by 2^n once at the very end
// when we return a floating point value
v = new ulong[n];
// store the scale factor 1 / 2^n
f = 1.0 / ((double)(((ulong)1) << n));
// the first few "directions" are given by the initialization seeds
// the number of seed values must equal the degree of the primitive polynomial
if (m.Count != s) throw new InvalidOperationException();
for (int i = 0; i < s; i++)
{
// seeds must be odd and the ith must be less than 2^i
if ((m[i] % 2 == 0) || (m[i] > (((ulong)1) << (i + 1)))) throw new InvalidOperationException();
// the values are m_i / 2^i, but remember we then scale up by 2^n
v[i] = m[i] << (n - (i + 1));
}
// The remainder of the "directions" are constructed via the recurrance
// u_i = u_{i-s} + 2^1 a_1 u_{i-1} + 2^2 a_2 u_{i-2} + \cdots + 2^{s-1} a_{s-1} u_{i-(s-1)} + 2^s u_{i-s}
// Note + in mod 2 arithmetic is XOR.
// Use v_i = u_i / 2^(i+1) * 2^n to translate this into a recurrence for the v's
// v_i = v_{i-s} 2^{-s} + a_1 v_{i-1} + a_2 v_{i-2} + \cdots + a_{s-1} v_{i-(s-1)} + v_{i-s}
// where the a's are the binary digits of a = (a_1 a_2 \cdots a_{s-1})
for (int i = s; i < n; i++)
{
// since the first and last coefficients are known to be one, we start with them
ulong vi = v[i - s] ^ (v[i - s] >> s);
// proceed through the bits of a, XORing in the appropriate value if the bit is 1
for (int j = 1; j < s; j++)
{
if (((a >> (s - j - 1)) & 1) != 0)
{
vi ^= v[i - j];
}
}
v[i] = vi;
}
}
// degree of primitive polynomial (i.e. degree of recurrsion)
int s;
// polynomial coefficients, expressed
ulong a;
// the number of "directions"
// the maximum number of values in the sequence is 2^n
private const int n = 31;
// the "directions"
ulong[] v;
// the list of "initial direction numbers"
ulong[] m;
// the factor to convert a given value to a floating point number on (0,1)
double f;
// our positition in the sequence
// p is the count
// q stores the "state" of the system
uint p = 0;
ulong q = 0;
public double Current => f * q;
public bool MoveNext()
{
// get index of first zero binary digit of p = (\cdots p_2 p_1 p_0)
int i = 0;
while (((p >> i) & 1) != 0) i++;
q ^= v[i];
p++;
return true;
}
public void Reset()
{
p = 0;
q = 0;
}
IEnumerator IEnumerable.GetEnumerator()
{
return new SobolEnumerator<float>(this);
}
public IEnumerator<float> GetEnumerator()
{
return new SobolEnumerator<float>(this);
}
}
//other file
public static void Generate(in int dimension, in int count, out List<float> values)
{
var p = SobolSequenceParameters.sobolParameters[dimension];
var seq = new SobolSequence(p.Dimension, p.Coefficients, p.Seeds);
values = seq.Take(count).ToList();
}
//other file
internal class SobolSequenceParameters
{
private SobolSequenceParameters(int dimension, ulong coefficients, ulong[] seeds)
{
this.Dimension = dimension;
this.Coefficients = coefficients;
this.Seeds = seeds;
}
public int Dimension { get; private set; }
public ulong Coefficients { get; private set; }
public ulong[] Seeds { get; private set; }
//http://web.maths.unsw.edu.au/~fkuo/sobol/
public static readonly SobolSequenceParameters[] sobolParameters = new SobolSequenceParameters[]
{
new SobolSequenceParameters(1, 0, new ulong[] { 1 }),
new SobolSequenceParameters(2, 1, new ulong[] { 1, 3 }),
new SobolSequenceParameters(3, 1, new ulong[] { 1, 3, 1 }),
new SobolSequenceParameters(3, 2, new ulong[] { 1, 1, 1 }),
new SobolSequenceParameters(4, 1, new ulong[] { 1, 1, 3, 3 }),
new SobolSequenceParameters(4, 4, new ulong[] { 1, 3, 5, 13 }),
new SobolSequenceParameters(5, 2, new ulong[] { 1, 1, 5, 5, 17 }),
new SobolSequenceParameters(5, 4, new ulong[] { 1, 1, 5, 5, 5 }),
new SobolSequenceParameters(5, 7, new ulong[] { 1, 1, 7, 11, 19 }),
new SobolSequenceParameters(5, 11, new ulong[] { 1, 1, 5, 1, 1 }),
new SobolSequenceParameters(5, 13, new ulong[] { 1, 1, 1, 3, 11 }),
new SobolSequenceParameters(5, 14, new ulong[] { 1, 3, 5, 5, 31 }),
new SobolSequenceParameters(6, 1, new ulong[] { 1, 3, 3, 9, 7, 49 }),
new SobolSequenceParameters(6, 13, new ulong[] { 1, 1, 1, 15, 21, 21 }),
new SobolSequenceParameters(6, 16, new ulong[] { 1, 3, 1, 13, 27, 49 })
};
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
//TestCode
[Button]
private void GenerateCubesViaSobol()
{
int SampleCount = 5000;
SobolSequenceGenerator.Generate(7, SampleCount, out var values_x);
SobolSequenceGenerator.Generate(9, SampleCount, out var values_y);
SobolSequenceGenerator.Generate(8, SampleCount, out var values_z);
currentRoutine = GenerateCubes();
IEnumerator GenerateCubes()
{
for (int i = 0; i < SampleCount; ++i)
{
var instance = GameObject.CreatePrimitive(PrimitiveType.Cube);
var pos = new Vector3(values_x[i], values_y[i], values_z[i]);
instance.transform.position = pos;
instance.transform.localScale = Vector3.one * 10f / SampleCount;
instances.Add(instance);
yield return null;
yield return null;
}
}
}
소볼의경우 a - coefficients, m- init direction에 따라 값이 달라지는데,
샘플에 사용된 s,a,m는 다음과 같습니다.
1
2
3
new SobolSequenceParameters(5, 4, new ulong[] { 1, 1, 5, 5, 5 }), //(x)
new SobolSequenceParameters(5, 7, new ulong[] { 1, 1, 7, 11, 19 }),//(z)
new SobolSequenceParameters(5, 11, new ulong[] { 1, 1, 5, 1, 1 }), //(y)
 xz → xy → yz 화면으로 회전합니다
xz → xy → yz 화면으로 회전합니다
꼬리
이거 2022년도에 기능으로 구현해서 넣고 2년뒤에서야 gif 파일목록 구경하다가 찾아서 작성합니다 ㅎ….
오랜만에 또 구현하니까 재미있네요
